From Nicotine to None: WHO’s Comprehensive Plan to Help Smokers Quit
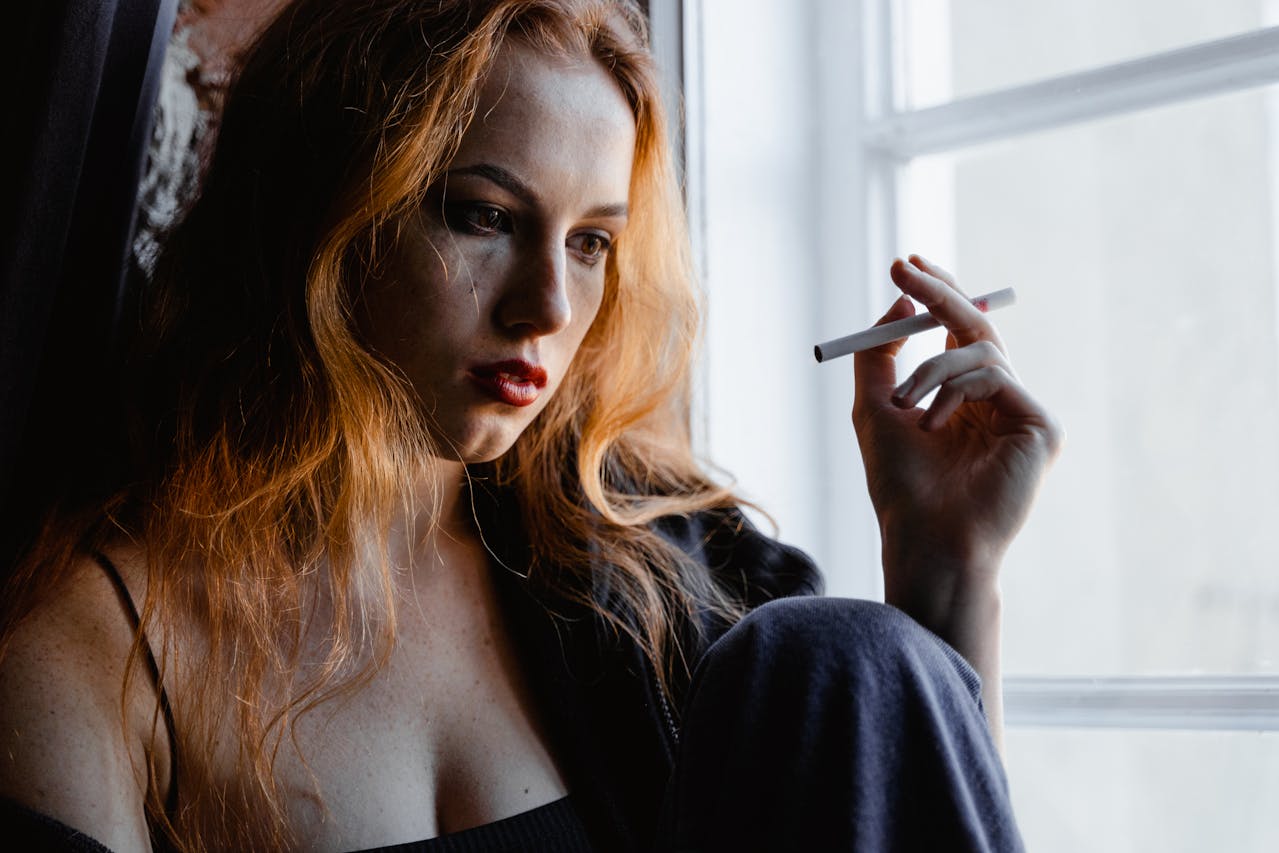

The World Health Organization (WHO) has unveiled its first-ever clinical treatment guideline for tobacco cessation in adults, marking a significant step in the global fight against tobacco-related diseases. This guideline is designed to help the over 750 million tobacco users worldwide who want to quit. It provides a comprehensive set of interventions, including behavioral support from healthcare providers, digital cessation tools, and pharmacological treatments.
Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General, emphasized the importance of this guideline, stating that it equips countries with essential tools to support individuals in quitting tobacco and reducing the global burden of tobacco-related illnesses. The guideline is relevant for all adults seeking to quit various forms of tobacco, such as cigarettes, waterpipes, smokeless tobacco, cigars, roll-your-own tobacco, and heated tobacco products.
Despite more than 60% of the world’s 1.25 billion tobacco users wanting to quit, a staggering 70% lack access to effective cessation services due to resource constraints within health systems. Dr. Rüdiger Krech, Director of Health Promotion at WHO, highlighted the immense struggle individuals face when trying to quit smoking, noting the strength and suffering involved in overcoming this addiction. The guidelines aim to provide communities and governments with the best possible support for those on this challenging journey.
Effective tobacco cessation requires a combination of pharmacotherapy and behavioral interventions. The WHO recommends making these treatments available at no or reduced cost, especially in low- and middle-income countries, to improve accessibility. Key pharmacological treatments endorsed by the WHO include varenicline, Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT), bupropion, and cytisine.
To enhance global access to recommended tobacco cessation medications, WHO initiated a prequalification procedure for medicinal products in 2023. In April 2024, Kenvue’s nicotine gum and patch became the first WHO-prequalified NRT products, setting a precedent for future approvals.
Behavioral interventions play a crucial role in helping individuals quit tobacco. WHO recommends brief health worker counseling, lasting from 30 seconds to three minutes, to be offered routinely in healthcare settings. For those interested in more intensive support, individual, group, or phone counseling can be highly effective. Additionally, digital interventions such as text messaging, smartphone apps, and internet programs can serve as valuable tools for self-management or as adjuncts to other treatments.
WHO urges healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders to adopt and implement this guideline to promote tobacco cessation and improve the health of millions of people worldwide. By doing so, we can take a significant step towards reducing the devastating impact of tobacco use on global health.
This comprehensive approach outlined by WHO is a beacon of hope for millions striving to quit tobacco. By integrating behavioral support, digital tools, and effective medications, we can offer the necessary assistance to those who need it most. It’s a call to action for healthcare systems, policymakers, and communities to embrace these guidelines and work together to create a healthier, tobacco-free world.